The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is a fundamental financial metric used by investors to assess a company’s valuation relative to its earnings. It provides insights into how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. In addition to the P/E ratio, the Forward P/E ratio takes into account future earnings estimates, offering a forward-looking perspective. In this article, we will delve into what the P/E ratio and Forward P/E ratio are, why they matter, and provide real-life examples using two prominent companies: Apple Inc. and Tesla, Inc.
What Is the P/E Ratio?
The P/E ratio, or Price-to-Earnings ratio, is calculated by dividing a company’s stock price per share by its earnings per share (EPS). It is expressed as follows:
![]()
The P/E ratio is a widely used metric that helps investors gauge a company’s valuation in relation to its current earnings. It reflects market sentiment and expectations about a company’s future prospects.
Why Does the P/E Ratio Matter?
The P/E ratio matters for several reasons:
- Valuation: It provides a quick assessment of whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. A higher P/E ratio may indicate an overvalued stock, while a lower P/E ratio may suggest undervaluation.
- Comparative Analysis: Investors use the P/E ratio to compare the valuations of different companies within the same industry or sector. It helps identify relative bargains or expensive stocks.
- Investor Sentiment: A high P/E ratio can reflect strong investor confidence and expectations of future growth. Conversely, a low P/E ratio may signal concerns about a company’s prospects.
Real-Life Example: P/E Ratio for Apple Inc. and Tesla, Inc.
As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, let’s examine the P/E ratios for Apple Inc. and Tesla, Inc. using hypothetical figures:
– Apple Inc. (AAPL):
– Stock Price: 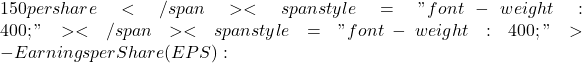 5 per share (based on trailing 12-month earnings)
5 per share (based on trailing 12-month earnings)
– P/E Ratio for Apple: ![]() 5 = 30
5 = 30
– Tesla, Inc. (TSLA):
– Stock Price: 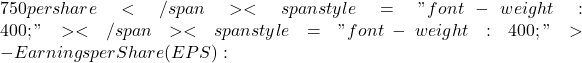 2 per share (based on trailing 12-month earnings)
2 per share (based on trailing 12-month earnings)
– P/E Ratio for Tesla: ![]() 2 = 375
2 = 375
In this example, Apple has a P/E ratio of 30, indicating that investors are willing to pay ![]() 375 for each dollar of Tesla’s earnings. This stark difference reflects the market’s perception of their respective growth prospects.
375 for each dollar of Tesla’s earnings. This stark difference reflects the market’s perception of their respective growth prospects.
What Is the Forward P/E Ratio?
The Forward P/E ratio, often simply referred to as the Forward P/E, is a variation of the traditional P/E ratio. Instead of using historical earnings, it incorporates future earnings estimates provided by analysts. The formula is the same as the P/E ratio, but it uses the estimated earnings for the next 12 months (or another specified period) in the denominator.
![]()
The Forward P/E provides a forward-looking perspective on a company’s valuation, taking into account expected future earnings.
Real-Life Example: Forward P/E Ratio for Apple Inc. and Tesla, Inc.
Continuing with our example:
– Estimated EPS for Apple Inc. (next 12 months): 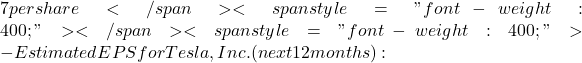 6 per share
6 per share
Now, let’s calculate the Forward P/E ratios:
– Forward P/E Ratio for Apple: ![]() 7 ≈ 21.43
7 ≈ 21.43
– Forward P/E Ratio for Tesla: ![]() 6 ≈ 125
6 ≈ 125
In this scenario, Apple’s Forward P/E ratio is approximately 21.43, indicating that investors are willing to pay $21.43 for each expected dollar of Apple’s earnings over the next 12 months. Tesla’s Forward P/E ratio, on the other hand, is approximately 125, reflecting the higher valuation investors are assigning to its future earnings.
Conclusion
The P/E ratio and Forward P/E ratio are valuable tools for investors to assess a company’s valuation and market sentiment. While the P/E ratio relies on historical earnings, the Forward P/E incorporates future earnings estimates, providing a forward-looking perspective. By examining real-life examples from companies like Apple Inc. and Tesla, Inc., investors can gain insights into how these ratios can help inform investment decisions in the dynamic world of finance. However, it’s crucial to consider other factors, such as industry dynamics and a company’s growth potential, when interpreting these ratios.
