Return on Equity (ROE) is a vital financial metric that provides a glimpse into a company’s ability to generate profits from shareholders’ equity. It serves as a key indicator of a company’s financial health and efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the concept of ROE and provide real-life examples from Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) and the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY).
What Is Return on Equity (ROE)?
Return on Equity is a financial ratio that assesses a company’s profitability by measuring the return generated from shareholders’ equity. It is calculated by dividing a company’s net income attributable to common shareholders by its average shareholder equity. The formula for ROE is as follows:
![]()
Typically expressed as a percentage, ROE signifies how effectively a company uses shareholders’ equity to generate earnings.
Why Does Return on Equity Matter?
ROE carries substantial importance for several reasons:
- Profitability Assessment: ROE provides insights into a company’s profitability. A higher ROE implies efficient utilization of equity to generate profits.
- Efficiency Indicator: It measures how efficiently a company employs its equity to generate income. A high ROE suggests effective operations and capital management.
- Comparative Analysis: Investors use ROE for benchmarking, allowing comparisons across companies or industry peers. It aids in evaluating a company’s financial performance.
- Investor Confidence: Consistently high ROE can bolster investor confidence. It reflects a company’s ability to yield returns on shareholders’ investments.
Real-Life Examples: ROE for AMD and SPY
Let’s examine the ROE for Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) and the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) using hypothetical figures based on data available as of my last knowledge update in September 2021.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD)
– Net Income (Trailing 12 Months): 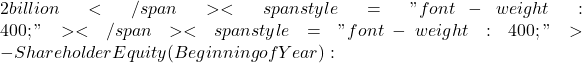 5 billion
5 billion
– Shareholder Equity (End of Year): $8 billion
To calculate the average shareholder equity:
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ Average Shareholder Equity = \frac{$5 billion + $8 billion}{2} = $6.5 billion \]](https://24stocknews.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0adc4e05f95b618e54fd37524fbc0367_l3.png)
Now, let’s calculate AMD’s ROE:
![]()
AMD’s ROE, in this example, is approximately 30.77%. This indicates that AMD generated a 30.77% return on the equity invested by its shareholders over the past year.
Return on Equity (ROE) serves as a critical metric for evaluating a company’s profitability and efficiency in leveraging shareholders’ equity. It aids investors in assessing financial performance and making informed investment decisions. By exploring real-life examples from Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) we gain valuable insights into how ROE can provide a meaningful perspective on financial health and the ability to deliver returns to shareholders. Keep in mind that ROE can vary among companies and financial instruments, and it’s most informative when used for comparative analysis within the same industry or category.
